5.3.7 Clipping and masking images - LUPMISManual
Main menu:
- 0. Introduction
- 1. GIS handling
-
2. GIS data entry
- 2.1 Create new layer
- 2.2 Digitize line
- 2.3 Digitize point
- 2.4 Digitize polygon
- 2.5 Edit existing layer
- 2.6 Delete feature
- 2.7 Split line
- 2.8 Split polygon
- 2.9 Merge lines from different layers
- 2.10 Unite lines
- 2.11 Snap lines
- 2.12 Join polygons
- 2.13 Extend polygon
- 2.14 Insert island
- 2.15 Define unit surrounding islands
- 2.16 Create 'doughnut'
- 2.17 Fill 'doughnut' polygon
- 2.18 Fill polygon with 'holes'
- 2.19 Digitize parcels from sector layout
-
3. GIS operations
- 3.1 Create buffer
- 3.2 Create exclusion zone
- 3.3 Overlay units
- 3.4 Convert line to polygon
- 3.5 Derive statistics (area size, length)
- 3.6 Clip unit according to other unit
- 3.7 Create geographic grid
- 3.8 Move entire vector map
- 3.9 Move or copy individual features on a map
- 3.10 Adjust polygon to line
- 3.11 Convert points to polygon
- 3.12 Define by distance
- 3.13 Create multiple objects
- 3.14 Transfer styles from one layer to another
-
4. Attribute database
- 4.1 Start with database
- 4.2 Import database
- 4.3 Display database information
- 4.4 Enter attribute data
- 4.5 Attribute matrix of multiple layers
- 4.6 Seeds
- 4.7 Repair attribute data
- 4.8 Merge lines with attached database
- 4.9 Transfer attribute data from points to polygons
- 4.10 Copy styles, labels, attributes
-
5. Conversion of data
-
5.1 Points
- 5.1.1 Import list of points from text file
- 5.1.2 Import list of points from Excel file
- 5.1.3 Convert point coordinates between projections
- 5.1.4 Convert point coordinates from Ghana War Office (feet)
- 5.1.5 Convert point coordinates from Ghana Clark 1880 (feet)
- 5.1.6 Track with GPS
- 5.1.7 Download GPS track from Garmin
- 5.1.8 Download GPS track from PDA
- 5.1.9 Frequency analysis of points
- 5.2 Vector maps
- 5.3 Raster maps
-
5.4 Communication with other GIS programs
- 5.4.1 Import GIS data from SHP format
- 5.4.2 Import GIS data from E00 format
- 5.4.3 Import GIS data from AutoCAD
- 5.4.4 Export LUPMIS data to other programs
- 5.4.5 Export GIS to AutoCAD
- 5.4.6 Change a shape file to GPX
- 5.4.7 Transfer GIS data to other LUPMIS installations
- 5.4.8 Digitize lines in Google Earth
- 5.5 Terrain data
- 5.6 Export to tables
- 5.7 Density map
-
5.1 Points
-
6. Presentation
- 6.1 Labels
- 6.2 Styles and Symbols
- 6.3 Marginalia
- 6.4 Legend
- 6.5 Map template
- 6.6 Final print
- 6.7 Print to file
- 6.8 3D visualization
- 6.9 External display of features
- 6.10 Google
-
7. GIS for land use planning
- 7.1 Introduction to land use planning
- 7.2 Land use mapping for Structure Plan
- 7.3 Detail mapping for Local Plan
- 7.4 Framework
- 7.5 Structure Plan
- 7.6 Local Plan
- 7.7 Follow-up plans from Local Plan
- 7.8 Land evaluation
-
8. LUPMIS Tools
- 8.1 General
-
8.2 Drawing Tools
- 8.2.1 Overview
- 8.2.2 UPN
- 8.2.3 Streetname + housenumbers
- 8.2.4 Lines
- 8.2.5 Arcs
- 8.2.6 Polygons
- 8.2.7 Points
- 8.2.8 Cut line
- 8.2.9 Other Drawing Tools
- 8.2.10 Import
- 8.2.11 Projections + conversions
- 8.2.12 Format conversion
- 8.2.13 Other GIS Tools
- 8.2.14 Utilities
- 8.3 Printing Tools
- 8.4 Permit Tools
- 8.5 Census Tools
-
8.6 Revenue Tools
- 8.6.1 Overview
- 8.6.2 Entry of revenue data
- 8.6.3 Retrieval of revenue data
- 8.6.4 Revenue maps
- 8.6.5 Other revenue tools
- 8.7 Reports Tools
- 8.8 Project Tools
- 8.9 Settings
-
9. Databases
- 9.1 Permit Database
-
9.2 Plans
- 9.2.1 Accra
- 9.2.2 Kasoa
- 9.2.3 Dodowa
- 9.2.4 Sekondi-Takoradi
-
9.3 Census Database
-
9.4 Revenue Database
-
9.5 Report Database
-
9.6 Project Database
- 9.7 Address Database
-
Annexes 1-10
- A1. LUPMIS setup
- A2. Background to cartography/raster images
- A3. Glosssary
- A4. Troubleshooting
- A5. Styles
- A6. Classification for landuse mapping/planning
- A7. GIS utilities
- A8. Map projection parameters
- A9. Regions / Districts
- A 10. Standards
-
Annexes 11-20
- A11. LUPMIS distribution
- A12. Garmin GPS
- A13. Training
- A14. ArcView
- A15. Population statistics
- A16. Entry and display of survey data
- A17. External exercises
- A18. Programming
- A19. Paper sizes
- A20. Various IT advices
- A21. Site map and references
5.3.8 Clipping and Masking Images
Level of expertise required for this Chapter: Advamced; general Map Maker training
Images can be too large (often, satellite images). It is then recommended to break it down into individual tile for easier and faster handling. You load only this one large image, which can take a long time, and define the frame:
1. Define a map frame
2. Calculate the frame (W, E, N, S)
3. Main menu > Utilities > Bitmap utilities > Mosaic and clip > Mosaic and clip calibrated bitmaps window: Add file (1, see below) > Select file type: JPG > Select folder and file > Open > and repeat for all files, you want to bring together > Define frame: Min X for west (2) > Min y for south > Max x for east > Max y for north > Check the red frame, which appears on the display > Check that Map Maker calibration is ticked (3) > OK (4) > Select file type: Recommended at LUPMIS is JPG > Specify new file name, preferably according to the map index > Save
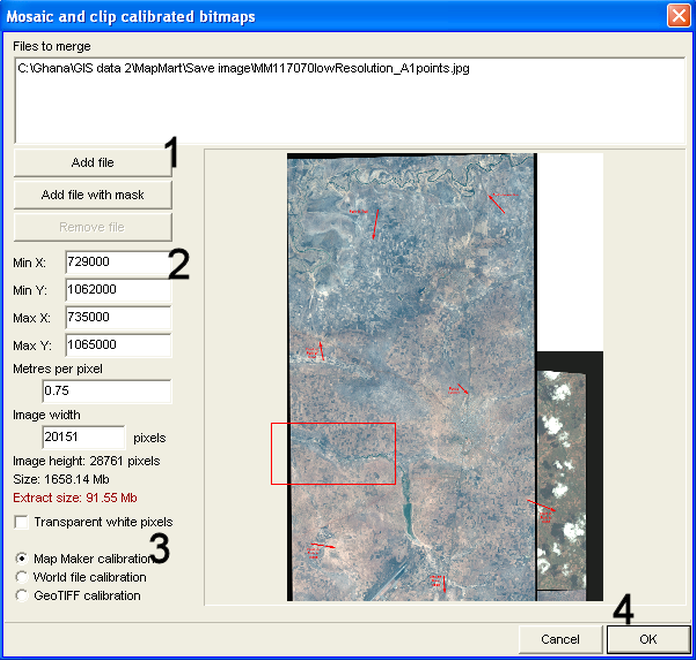
- - - - -
If the ‘frame’ can‘t be defined by coordinates (min and max x and y), but has an irregular shape, the masking tool can be applied.
Digitize the polygon of this irregular shape, which you want to ‘keep’, in Map Maker, and save it as a DRA file. All areas outside this polygon will not be copied to the new image.
In the Mosaic and clip calibrated bitmaps window, you don’t select ‘Add file’, but ‘Add file with mask’. After selecting the image (as explained above), you will be asked to enter the ‘mask’. All further processing will be the same.

